How to Charge a Scosche 500K Micro Farad Capacitor | Showing Various Ways
A Scosche 500K µF capacitor will reach a 99% charge after 5-time constants and 63.2% after just one time constant. The time constant is calculated using the formula t = R*C. You have to apply a DC voltage across the capacitor to charge it.
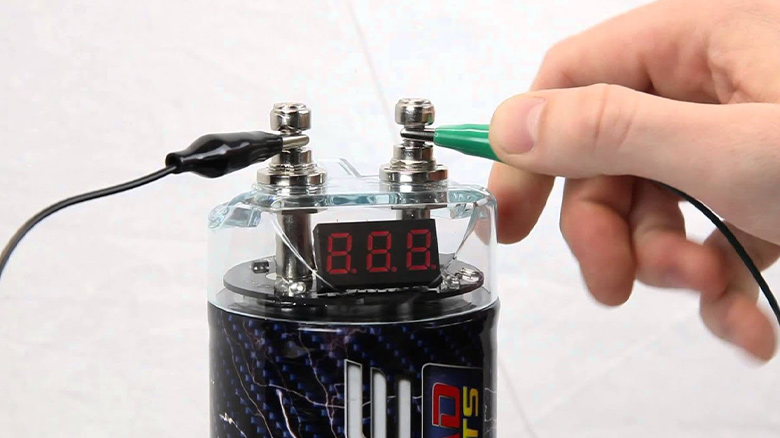

The Scosche 500K micro-farad capacitor reserves reserve system power to improve your audio system’s bass response. For increased strength, the capacitor comes with an impact-resistant tinted polycarbonate cover. It has an LCD Digital Voltage Display for convenient system monitoring.
How to Charge a Scosche 500K Micro Farad Capacitor?
You can connect a DC voltage and a resistor or a light with your Scosche 500K Micro Farad capacitor to charge it. The connection forms an RC circuit. Hence the capacitor will charge up gradually through the resistor until the voltage across it reaches that of the supply voltage.
A Scosche 500K Micro Farad capacitor is used in the DC power reservoir for a car audio setup. If you listen to loud music frequently, capacitors protect amplifiers from potentially dangerous under-voltage surges. However, the main reason for installing capacitors is to keep your car’s voltage steady.
How Do You Charge a Farad Capacitor?
It is fairly simple to charge a capacitor. Connecting a capacitor to a DC power source charges it. This could be a battery or a direct current power supply. Once connected to the DC voltage source, the capacitor will charge to the voltage output by the DC voltage source.
You must connect a resistor or test light between the DC voltage source and the capacitor to charge it. Connect the circuit like the following figure.
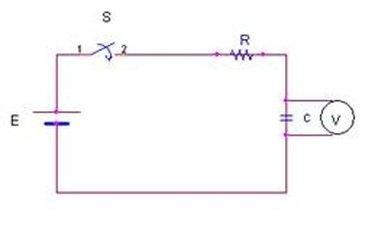
Using a Test Light
The simplest technique to charge a capacitor is with a test light. All you have to do is connect the test light’s power and ground to where your fuse used to be. To make this operation easier, use alligator clips. Hold the test light in place of the fuse until the light bulb goes out. Your capacitor has been charged when the light goes off.
Using a Resistor
Unless otherwise specified, you will require a 1-watt, 30 – 1,000 Ohm (1kohm) resistor to charge your capacitor (your capacitor may have a resistor included). Use a higher impedance resistor to ensure that the capacitor charges slowly. This will keep the capacitor from charging too quickly and causing harm.
How Do You Charge a Capacitor?
A capacitor can be charged simply by connecting it to an electric circuit. When you switch on the electricity, an electric charge slowly accumulates on the plates. One plate receives a positive charge, while the other receives an equal and opposite (negative) charge.
How Do You Charge a Capacitor Without a Resistor?
You can use an inductor, a PSU controller chip or an LED in place of a resistor to charge your capacitor.
Using an Inductor
An inductor can be used in place of a resistor to charge the capacitor with a diode connected in series with the inductor. The capacitor and the inductor form a series resonant circuit. Once the capacitor gets charged fully, the diode gets open-circuited disconnecting the capacitor from the circuit.
Using a PSU Controller Chip
As we know the function of the resistor to charge a capacitor is to control the current, hence a PSU controller chip could be used in place of a resistor. The PSU controller chip works as a current controller and some energy dissipates.
Another method of charging a capacitor without a resistor is to ensure that the voltage across the capacitor is more than its rated voltage. Thus, the capacitor will get fully charged to a voltage less than the applied voltage across it. This ensures that the capacitor is charged fully when it’s disconnected from the circuit.
Using an LED
If a resistor isn’t used it’s necessary to connect an LED in place of the resistor. It’d keep glowing when the capacitor is charging and would stop glowing once the capacitor is fully charged. Or an AC signal could be used as a source, as it has a frequency that allows the signal to pass across the capacitor.
In practical cases, there exists an internal resistance of the source, wires, and also capacitors used in circuits. So, even if resistors aren’t used, the capacitor charges. But it’s more convenient to use a circuit resistor to control the capacitors’ charging and discharging.
How Do You Charge a Small Capacitor?
All capacitors are often made up of two conductors close to one other and separated by an insulator. The common capacitor values range from picofarads to nanofarads to microfarads. To charge such small capacitors the methods to be followed are quite the same as farad capacitors.
You must connect a resistor or test light between the battery and the capacitor to charge it. A multimeter should be used to measure the voltage of the capacitor before, during, and after discharge. The time required for the capacitor to be fully charged is equivalent to about 5-time constants or 5T.
Conclusion
Generally, the charge is not stored in capacitors. Capacitors store a charge imbalance. If one plate of a capacitor stores one coulomb of charge, the second plate will also store one coulomb, resulting in a total charge (added up across both plates) of zero.

![[Explained 4 Facts] Do Capacitors Expire?](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/do-capacitors-expire-768x431.webp)
![Can I Use 25V Capacitor Instead of 35V? [Technically Explained]](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Can-I-Use-a-25V-Capacitor-Instead-of-35V-768x431.webp)

![[Answered & Explained] Does Size Matter in Capacitor?](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Does-Size-Matter-in-Capacitor-768x431.webp)

This video is very helpful to me thanks
You’re welcome! I’m glad to hear that you found the video helpful. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, feel free to ask.