[Easy Explanation] Do Resistors Have a Max Voltage?
When it comes to regulating current flow inside a circuit, resistors are essential parts of electronics. To accommodate varied applications, they are available in a variety of forms, dimensions, and features.
When working with resistors, a frequent query is if they have a maximum voltage rating. In this article, we’ll explore the principles of resistors and their behavior in electronic systems to discover the answer to that query.
How To Calculate The Maximum Voltage Of A Resistor?
A resistor is an electrical component that prevents electricity from passing through a circuit by adding resistance in ohms (Ω). Its value affects the current flow. Resistors are used in limited voltages and currents, but there is no safe maximum voltage for their operation.
The maximum voltage rating of a resistor depends on its power rating and ambient temperature. Its maximum working voltage is 1.5 times its power rating. Common through-hole resistors range from 200 to 1000 volts, while high-voltage resistors can tolerate up to a few kilovolts. Follow manufacturer instructions for safe operation, even using specialty resistors.

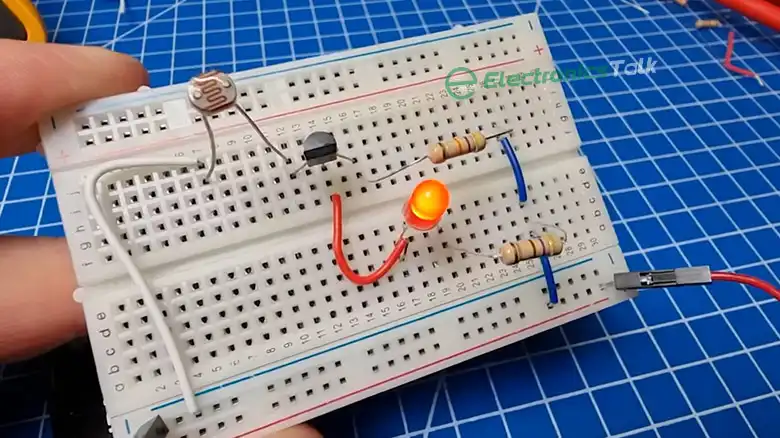
Figure 01: Resistors
Understanding the relationship between voltage, current, resistance, and power is necessary to calculate the maximum voltage for resistors. A resistor’s power rating and physical attributes define the highest voltage it can withstand. The power equation may be used to generate the formula for calculating the maximum voltage for a resistor:
Power (P) = Voltage (V) × Current (I)
Solving for voltage gives:
Voltage (V) = Power (P) / Current (I)
A resistor’s power rating (Pmax), which represents the maximum power it can dissipate, can be used in the formula:
Maximum Voltage (Vmax) = Power Rating (Pmax) / Current (I)
Now, we can apply Ohm’s law to determine the current flowing through the resistor:
Voltage (V) = Current (I) × Resistance (R)
Solving for current gives:
Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
Substituting this current value into the previous equation:
Maximum Voltage (Vmax) = Power Rating (Pmax) / (Voltage (V) / Resistance (R))
Simplifying further:
Maximum Voltage (Vmax) = Power Rating (Pmax) × Resistance (R) / Voltage (V)
The maximum voltage a resistor can tolerate without going above its power rating is determined by this formula. We must keep in mind that a resistor’s power rating, which is often provided by the manufacturer, specifies the maximum amount of power the device can output without overheating or causing damage to its internal components.
Factors Affecting Maximum Voltage Ratings
The maximum voltage rating of a resistor is influenced by its design, construction materials, and intended usage, determining its ability to withstand voltage stress without failure. Key factors include:
- Materials: The voltage rating of a resistor is significantly influenced by the materials used in its manufacturing. The electrical and thermal characteristics of various materials influence how well they can handle high voltages. For instance, resistors with high voltage ratings are more likely to be manufactured of materials with superior insulation qualities.
- Insulation: The resistor’s capacity to withstand high voltages is influenced by the insulating materials that are employed to cover or encase it. High-quality insulation lowers the possibility of arcing or failure when exposed to high voltage.
- Physical Size: The voltage rating of a resistor may be affected by its size. Larger resistors frequently have larger heat-dissipating surface areas, which may enable them to withstand higher voltages without overheating.
- Construction Design: The resistor’s internal design and arrangement may have an impact on its voltage rating. Higher voltage ratings may be influenced by design elements that lower electric field concentrations, lessen the possibility of corona discharge, and offer efficient heat dissipation.
- Dielectric Strength: The term “dielectric strength” describes a material’s capacity to tolerate electric stress without degrading. greater voltage ratings for resistors are probably due to their use of materials with greater dielectric strengths.
It’s crucial to remember that these variables interact with one another, and manufacturers take them all into account when establishing the maximum voltage rating of a resistor. Users should always refer to the datasheets and instructions provided by the manufacturer to ensure correct resistor selection and usage depending on their voltage needs.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers – FAQs
What happens if I exceed the maximum voltage rating of a resistor?
A resistor’s maximum voltage rating should never be exceeded for a variety of reasons. The resistor can begin to conduct too much current, get too hot, or even start to arc internally. In severe circumstances, this may result in the burnout of the resistor, potentially causing harm to the nearby circuit components.
Can I increase the maximum voltage rating of a resistor through cooling or other methods?
Cooling techniques could be able to reduce heat-related problems, but they might not considerably raise a resistor’s voltage rating. Instead of depending exclusively on cooling to overcome voltage constraints, it is advisable to select resistors with voltage ratings that fit the needs of your circuit.
Are there any specific applications where understanding the maximum voltage ratings of resistors is crucial?
Yes, careful selection of resistors with the proper voltage ratings is necessary for applications like power supply, high-voltage circuits, and electrical systems that are vulnerable to voltage surges. Circuit failure or malfunction can occur if these ratings are not taken into account.
To Conclude
Designing dependable circuits requires understanding electronics’ limitations, as resistors have maximum voltage ratings. Overcoming these limits can damage or degrade operations. Engineers and hobbyists can protect electronic systems’ integrity by adhering to manufacturer requirements and recommendations, ensuring safe working conditions for resistors.




![[10 Methods] How Do I Know if My Op Amp Is Unity Gain Stable?](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/How-Do-I-Know-if-My-Op-Amp-Is-Unity-Gain-Stable-768x431.webp)
![[4 Methods Explained] How Is Winding Capacitance Measured?](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/How-Is-Winding-Capacitance-Measured-768x431.webp)