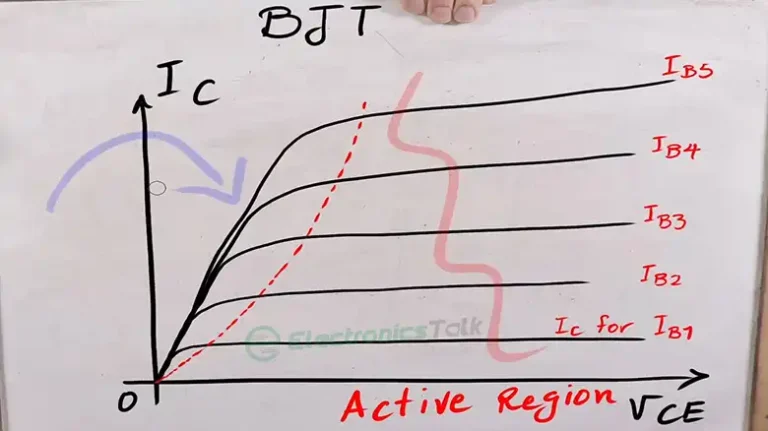
What Is the Difference Between 1N4001 and 1N4003? Briefly Explained
Both varieties of 1N4001 and 1N4003 diodes are often used in electronic circuits. Their ability to handle voltage is where they most significantly diverge from one another. The maximum repetitive reverse voltage (VRRM) of 1N4001 and 1N4003 diodes are different.
The 1N4001 should be adequate if you’re working on a circuit with minimal voltage requirements. To make sure the diode can withstand the necessary voltage levels, it is advised to utilize the 1N4003 if your circuit requires greater voltages.

1n4001 vs 1n4003 | Major Comparison
General-purpose rectifier diodes from the 1N400x series are frequently utilized in a variety of electrical circuits. These diodes are made by several different manufacturers, each of which may have somewhat varying specs, as indicated by the “1N” prefix. The designation’s “400x” portion identifies the particular type within the series.
The peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating of the 1N4001 and 1N4004 diodes is the primary distinction between them. The reverse voltage rating of the 1N4001 is 50 volts, whereas the reverse voltage value of the 1N4003 is 200 volts. This indicates that the 1N4003 can withstand a higher reverse voltage before failing.
The only difference between the 1N4001 and 1N4003 diodes is their reverse voltage rating. Both of them have a 1 amp forward current rating and a 30 amp peak forward surge current rating. They have the same reverse leakage current and forward voltage drop as well. The primary variations between the two diodes are listed in the following table:
| Characteristics | 1N4001 | 1N4003 |
| Peak inverse voltage (PIV) | 50V | 200V |
| Forward Current Rating | 1 A | 1 A |
| Peak forward surge current rating | 30 A | 30 A |
| Typical forward voltage drop | 1.1 V | 1.1 V |
| Reverse leakage current | 5 μA | 5 μA |
Applications of 1N4001 and 1N4003
The individual application will determine which diode you select. The 1N4001 is a suitable option if you require a diode that can resist a reverse voltage of up to 50 volts. The 1N4003 is a suitable option if you require a diode that can withstand a reverse voltage of up to 200 volts. Examples of uses for the 1N4001 and 1N4003 diodes are given below:
1N4001
- Power supplies
- Rectifier circuits
- Freewheeling diodes
1N4003
- Bridge rectifiers
- Motor control circuits
- High voltage applications
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
Q1. Do I Need to Take Any Special Safety Precautions When Using These Diodes?
It’s crucial to make sure that your circuit does not go above the diode’s maximum reverse voltage (VRRM). Potential damage can result from using a diode that has a lower VRRM than necessary. Take into account your application’s forward current requirements as well.
Q2. Is It Possible to Use a 1n4001/1n4003 as a Flyback Diode for an Inductor or Relay?
A 1N4001 or 1N4003 diode can be used as a flyback diode for an inductor or relay. There are a few things to keep in mind, though such as the switching duration, forward current rating, and reverse voltage rating.
Q3. What Physical Differences Can Be Found Between the 1n4001 and 1n4003 Diodes?
Physically, the 1N4001 and 1N4003 diodes are the same. Both of them are housed in the identical DO-41 (DO-204AL) packaging, which is a compact, cylinder-shaped device with axial leads.
Conclusion
Electronic components like the 1N4001 and 1N4003 diodes are frequently utilized in rectification circuits. Their greatest reverse voltage capabilities are what set them apart. When working with electronic components, always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and datasheets for exact information and instructions.

![Why Base Current is Weak Then Collector Current? [Answered]](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Why-is-Base-Current-Weaker-Than-Collector-Current-768x431.webp)