Do LED Resistors Get Hot? A Brief Explanation
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) do not produce much heat themselves, compared to traditional incandescent or fluorescent lights. However, the resistors used in LED circuits, commonly known as current-limiting resistors, can generate some heat. It usually depends on the amount of current they are handling and their power rating.
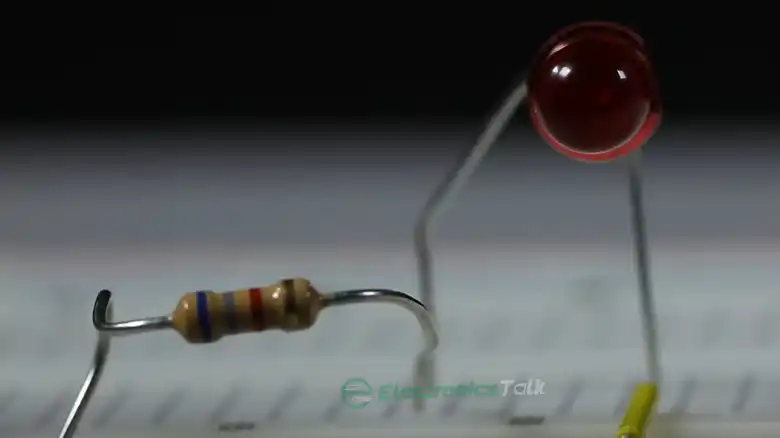
Is It Normal For LED Resistors To Get Hot?
It is normal for LED lights to get warm or even hot to the touch during operation. Where traditional incandescent bulbs emit light by heating a filament until it glows, LEDs produce light through the electroluminescence process.
In this process, electrons pass through a semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of light. Some of this energy is also released as heat. Therefore LED gets hot.
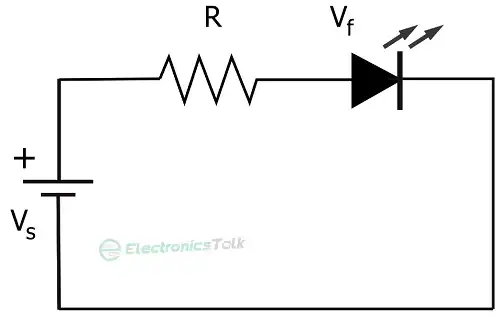
Figure 1: A circuit diagram with a LED and a resistor
In the circuit above, let the current through the diode be I and the voltage across the resistor be V. If the resistance is R ohm, then the power of the resistor,
P=VI=IR×I=I2R
From the equation, if the current increases, so does the power through the LED resistor. As some of the energy gets released as heat energy, more current will result in more heat making the LED resistor hot.
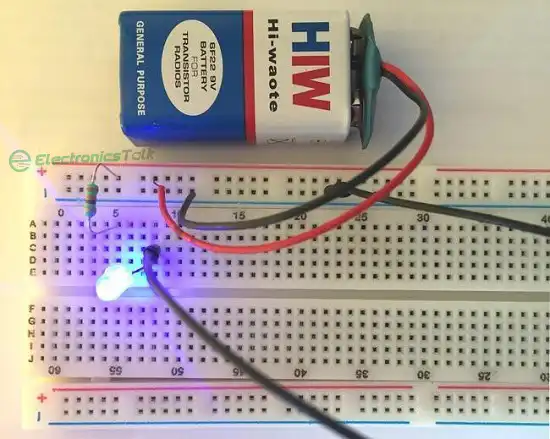
Figure 2: A circuit diagram with a LED and a resistor on breadboard.
How Hot Is Too Hot For a Resistor?
The temperature at which a resistor becomes “too hot” depends on its construction, materials, and intended usage. Generally, resistors have a specified maximum operating temperature, beyond which their performance can be negatively affected or even lead to failure.
This maximum temperature is often referred to as the “maximum junction temperature.”
For common through-hole resistors, like carbon composition or metal film resistors, should be below 125°C (257°F) to ensure stable and reliable performance.
For more specialized resistors, such as high-power or surface-mount resistors, the maximum operating temperature might be higher, around 150°C (302°F) or even more.
However, it’s always essential to refer to the datasheet or specifications provided by the manufacturer for accurate information about the specific resistor’s temperature limits.
Is It Normal For a Resistor To Get Hot?
Yes, it is normal for a resistor to get warm or even hot during operation as it dissipates power. Resistors work by converting electrical energy into heat according to Ohm’s law,
P=I2R
Where “P” is power, “I” is current, and “R” is resistance. When current flows through a resistor, a portion of that electrical energy is converted into heat energy due to the resistance of the material. Therefore it’s normal for a resistor to get hot.
How Do You Keep a Resistor From Getting Hot?
To prevent a resistor from getting too hot, several steps can be taken to manage its heat dissipation effectively. Here are some strategies you can use:
Choose the Right Resistor
A resistor with an appropriate power rating should be chosen for the application. Making sure the power rating of the resistor is higher than the power it will be dissipating ensures that the resistor can handle the heat generated without becoming excessively hot.
Use Higher-Value Resistors
Higher resistance values will result in lower current flow, reducing power dissipation and heat generation. Using multiple resistors in series or parallel configurations can help distribute the power dissipation, preventing any single resistor from getting too hot.
Heat Sinks
Heat sinks can be attached to the resistor to increase its surface area for heat dissipation. it helps conduct heat away from the resistor and into the surrounding air more efficiently.
Airflow and Ventilation
Ensuring proper airflow around the resistor allows heat to dissipate. Adequate ventilation can help keep the resistor’s temperature within acceptable limits.
Thermal Pads
Thermal pads or thermal adhesives can be attached to the resistor to a metal surface or heat sink, facilitating better heat transfer.
Derating
Operating a resistor below its maximum rated power can help extend its lifespan and reduce the risk of overheating. For example, if a resistor is rated for 1 watt, using it at 0.5 watts will help keep it cooler.
Temperature Sensors
Integrating temperature sensors into the circuit to monitor the resistor’s temperature can be a good option. If it starts to exceed safe limits, automatic measures like reducing current or shutting down the circuit can be implemented.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers – FAQs
- Are LED Load Resistors Safe?
Yes, LED load resistors are generally safe when used correctly and in the appropriate applications. Maintaining cautions like proper installation, Electrical Safety, and maintaining the manufacturer’s guidelines will result in a safe and proper experience.
- Is It Normal For The LED To Get Too Hot?”
LEDs can become warm during operation, but they should not become excessively hot. LEDs work by emitting light when electrons recombine with electron holes within the semiconductor material.
This process is relatively efficient and produces less heat. In well-designed LED lighting systems, the heat generated should be minimal and not noticeable to the touch.
Conclusion
As the heat dissipating component, it’s normal for an LED resistor to get hot. Maintaining proper cautions and manufacturer guidelines can help the resistor be more efficient and less hot.
Proper circuit design, component selection, and consideration of heat dissipation are crucial to maintaining the performance and reliability of your electronic circuits.

![[Answered] Do I Need a Resistor for a Laser Diode?](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Do-I-Need-a-Resistor-for-a-Laser-Diode-768x431.webp)

![[Easy Explanation] Do Resistors Have a Max Voltage?](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Do-Resistors-Have-a-Max-Voltage-768x431.webp)
