Polyester vs Polypropylene Capacitors | Which One?
Polyester capacitors are used in blocking, bypassing, decoupling, and some noise suppression circuits. And polypropylene capacitors are used in high-frequency ac applications.
The primary distinction between polyester and polypropylene capacitors is their use. Capacitors used in high-frequency applications are made from polypropylene.
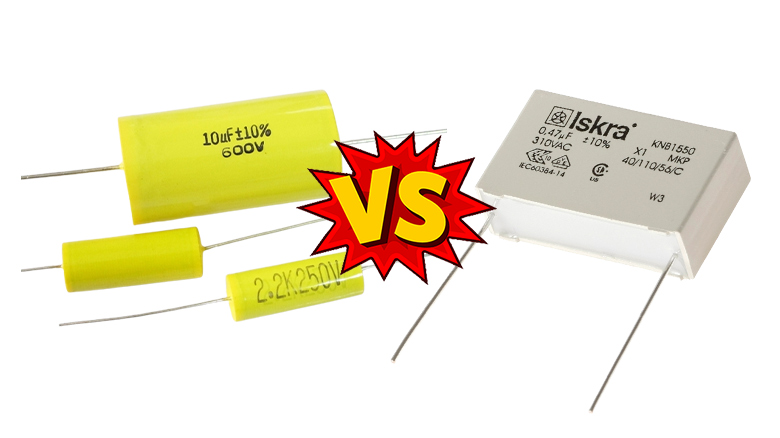
On the other hand, polyester capacitors are mostly employed for some fundamental functions and general applications. Polypropylene capacitors are more accurate than polyester capacitors in terms of accuracy.
Comparison Between Polyester vs Polypropylene Capacitors
Polyester film capacitors have a dielectric built of the polyester family’s thermoplastic polar polymer substance polyethylene terephthalate (PET), often known as Mylar. They come in metalized wrapped and stacked variants, as well as film and foil varieties.
On the other hand, capacitors with a dielectric constructed of polypropylene film are known as polypropylene capacitors. Polypropylene capacitors are available in a range of values from 100pf to 10F. Their high operating voltage is one of their most important characteristics.
Are Polypropylene Capacitors Good?
Polypropylene capacitors are good for many areas of applications for their key features.
Tolerance
When high levels of tolerance are necessary, these capacitors are frequently utilized.
Stability
Polypropylene capacitors have a low capacitance variation with time and voltage, making them appropriate for applications that need a constant amount of capacitance.
Capacitance Range
Polypropylene capacitors come in a variety of sizes and values. They are typically available in levels ranging from roughly 100pF to 10 nF and beyond.
Voltage Range
Capacitors made of polypropylene can withstand high voltages. Small capacitors with working voltages of 630V or even 1kV are typical, while 100V versions are also frequent.
Are Polyester Capacitors Good?
Polyester capacitors are also good for general purposes depending on their key features
Temperature
These capacitors may commonly work at temperatures up to 125°C due to the qualities of the polyester dielectric, however with a voltage de-rating.
Equivalent Series Resistance
Polyester capacitors are capable of delivering low equivalent series resistance.
High dV/dt
Since of the structure and dielectric of polyester, PET capacitors, they can be employed in applications with abrupt, quick rise time spikes because they can support high dV/dt values.
What are Polypropylene Capacitors Used For?
Polypropylene capacitors are used for various applications like
- Circuits for high-frequency pulse discharge
- Induction heating
- As AC capacitors for electrical distribution
- Sample and hold circuits
- Switching power supplies
- Precision timing circuits
- High-frequency resonant circuits
What Are Polypropylene Capacitors Used For?
Polyester capacitors are utilized in a variety of applications
- It’s used in a variety of low-frequency pulsing and DC circuits.
- Used in DC coupling, decoupling, and blocking applications.
- When the extremely high capacitance of electrolytic capacitors is not required, this capacitor is used in the power supply.
- Used in audio applications
- Used in noise suppression circuits
Are Polypropylene Capacitors Good for Audio?
Polypropylene versions are, in theory, the most ideal for audio applications because they have the lowest dissipation factor. Polypropylene capacitors can be used in practically any application.
Higher capacitance values are necessary for some applications, such as loudspeaker crossover networks. Polyester capacitors, which are made as special versions with a capacitance value of up to, can be used in certain instances as an exception.
Polyester has a larger dissipation factor than polypropylene, however, it is 20 times lower than equivalent audio frequency electrolytic capacitors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better polyester or polypropylene capacitors?
Polypropylene has a lower dielectric constant than polyester. Furthermore, thin-gauge films of this material are not accessible. Polypropylene is more costly than polyester and is not a good choice when the physical size of a component is important.
Conclusion
Polyester and polypropylene capacitors differ primarily in their use. Polypropylene capacitors are used for high-frequency applications, while polyester capacitors are used for general uses. Both capacitors have excellent performance in their respective fields.



![Can I Replace a 16V Capacitor With an 25V Capacitor? [7 Comparison Aspects Explained]](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Can-I-Replace-a-16V-Capacitor-With-a-25V-Capacitor-768x431.webp)

![Can I Use a 63V Capacitor Instead of 25V? [Technically Explained]](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Can-I-Use-a-63V-Capacitor-Instead-of-25V-768x431.webp)
![Can I Use 25V Capacitor Instead of 35V? [Technically Explained]](https://www.electronicstalk.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Can-I-Use-a-25V-Capacitor-Instead-of-35V-768x431.webp)